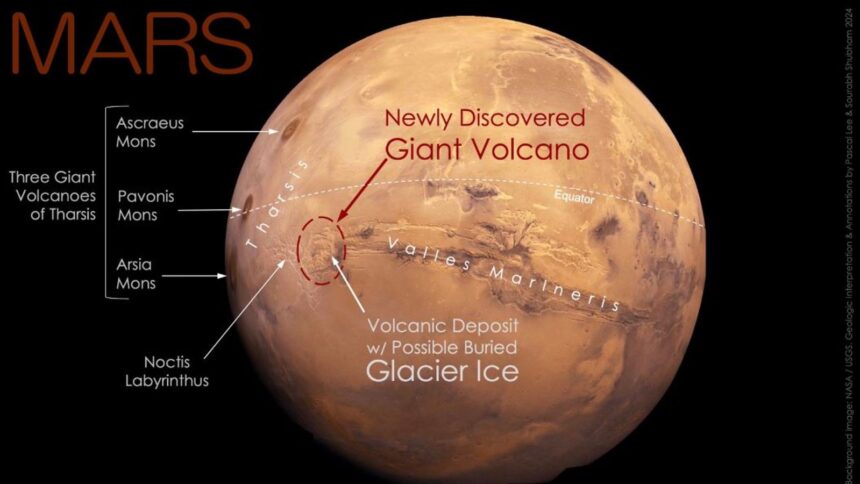
Scientists disclosed the volcano, which is 280 miles wide, at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference held in Texas on Wednesday. The volcano was discovered beside a potential sheet of buried glacial ice in the eastern section of Mars’ Tharsis volcanic province, close to the planet’s equator.
They said that although NASA’s circling spacecraft has seen the volcano numerous times since 1971, it was severely eroded and difficult to identify. It has been temporarily dubbed the Noctis volcano in honor of its location at the edge of the picturesque Noctis Labyrinthus (Labyrinth of the Night).
The scientists said in a research regarding the discovery that the volcano’s magnitude and “complex modification history” suggest it’s been active.